Canine Heartworm Disease is a fatal disease that poses a serious threat to the health of dogs. It is a thread-like parasite transmitted by mosquitoes, which lodges in the heart and pulmonary artery. The parasite can grow up to 30 centimeters in length and can survive for 5-7 years. Canine Heartworm can severely damage the heart and the inner walls of blood vessels, causing cardiopulmonary dysfunction in infected dogs. If left untreated, infected dogs may even die. It is the number one hidden killer of dogs!
How do dogs become infected with heartworm?
Canine heartworm is transmitted through mosquito bites. Canine heartworm disease has a high prevalence in areas with warm and humid climates. Dogs of any breed and age, whether indoors or outdoors, can be infected with canine heartworm throughout the year.
● Mosquitoes bite dogs that have been infected with canine heartworm, ingesting immature microfilariae during bloodsucking.
● After 2-3 weeks, the microfilariae develop into the infective third-stage larvae within the mosquito. At this point, if the mosquito bites another healthy dog, it will transmit the infective third-stage larvae to the healthy dog. The heartworm larvae penetrate the skin and migrate through tissues, entering the bloodstream and beginning to move towards the pulmonary artery and heart.
● After six months, it matures into an adult worm and becomes parasitic in the pulmonary artery and right ventricle, severely impairing the cardiopulmonary function of the infected dog. The mature female worm reproduces microfilariae, which enter the blood circulation of infected dogs.
What are the symptoms of a dog infected with heartworm?
Common symptoms include:
● Cough
● Lack of energy and decreased appetite
● Reduced exercise endurance, increased susceptibility to wheezing, and fatigue
● Dyspnea
● Severe infections may even lead to hemoptysis, anemia, ascites, heart, lung, liver, and kidney failure, and even death!
The initial clinical symptoms of heartworm infection in dogs are often mild, making it difficult for pet owners to detect. By the time obvious clinical symptoms appear, the condition is often already quite severe.
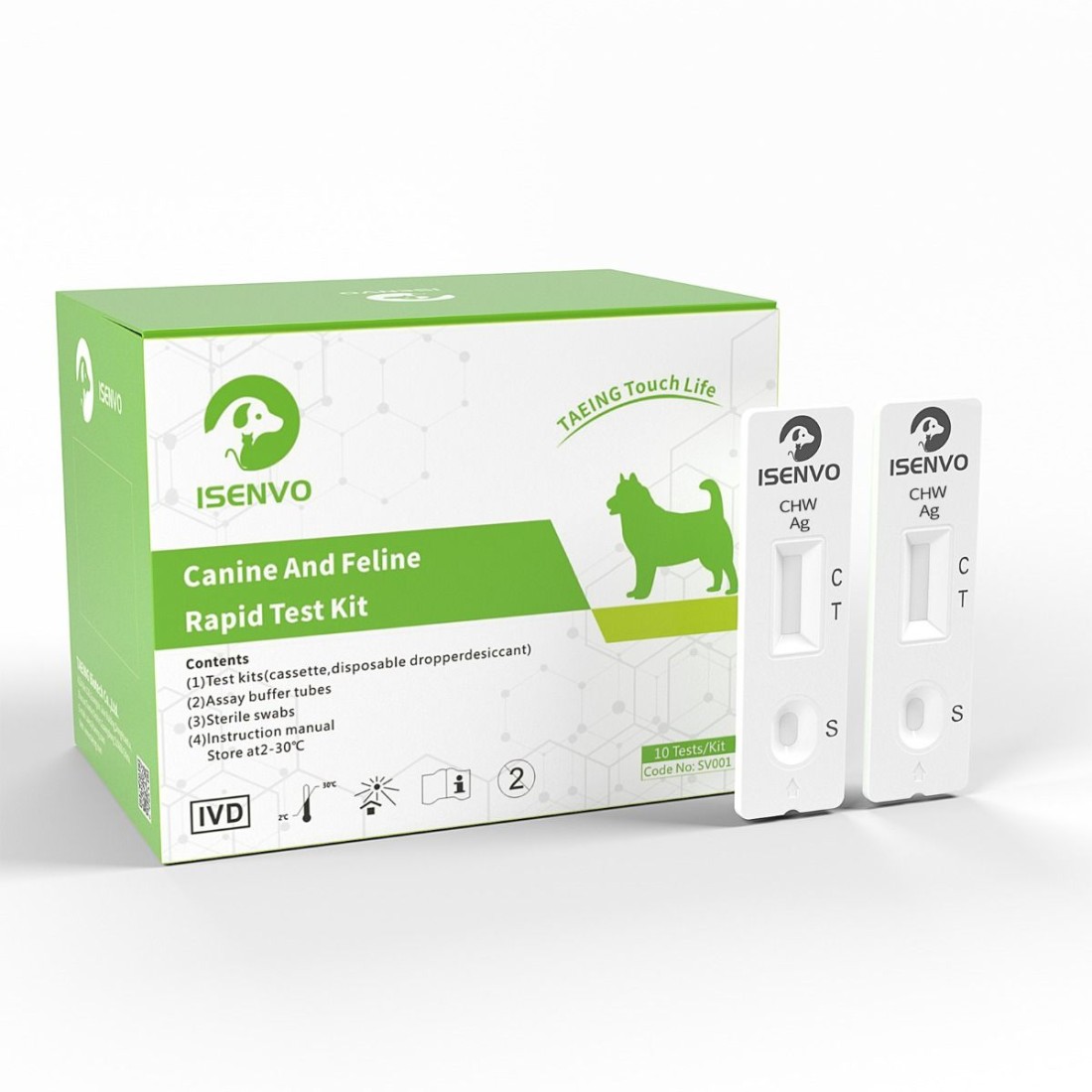
Rapid diagnostic test for canine heartworm
In diagnostic testing, heartworm antigen reagents often utilize colloidal gold immunochromatographic techniques (such as test strips) or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods. The Isenvo colloidal gold test strip is easy to operate, provides rapid results (within 10-15 minutes), requires no specialized equipment, and is suitable for primary veterinarians or on-site testing. Its sensitivity can reach over 95%.
Sample types typically include whole blood, serum, or plasma from dogs and cats. Whole blood samples can be directly used for strip testing without the need to separate serum, making them more suitable for rapid on-site applications; whereas serum or plasma samples are mostly used for laboratory testing.
How to protect dogs from the harm of canine heartworm?
Prevention is the best strategy to eradicate heartworm disease in dogs. Dogs can be infected with canine heartworm through mosquito bites at birth, so it is recommended that your beloved dog starts the canine heartworm prevention program from the age of 6 weeks.
Prevention is better than cure. Taking heartworm preventative medication for dogs every month is the safest, most economical, and simplest way to maintain your dog's health.








Validate your login